Exploring the intricate relationship between sleep and long-term brain health, this article delves into the fascinating ways in which our nightly rest impacts our cognitive functions and overall brain well-being.
As we uncover the importance of sleep in maintaining a healthy brain, we will discover how crucial it is to prioritize quality rest for optimal brain function.
Introduction to Sleep and Brain Health
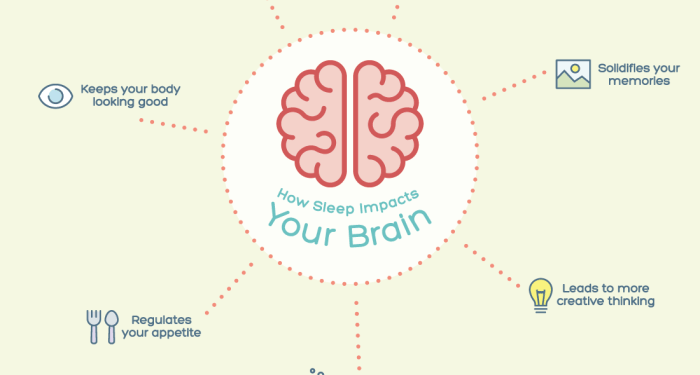
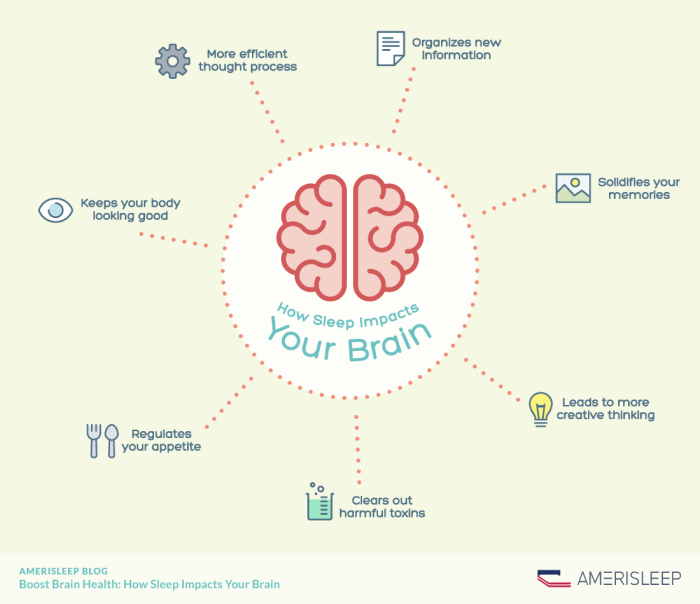
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining overall brain function and health. It is during sleep that the brain performs essential functions necessary for long-term well-being. Let's explore how sleep impacts the brain and influences various cognitive processes.
The Importance of Sleep for Brain Function
Sleep is essential for consolidating memories, promoting learning, and regulating emotions. During sleep, the brain processes information from the day and strengthens neural connections. Lack of sleep can impair cognitive function, attention, and decision-making abilities.
Mechanisms of How Sleep Affects Long-Term Brain Health
- During sleep, the brain clears out toxins and waste products that accumulate during waking hours, helping to prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
- Sleep is crucial for the production of neurotransmitters that regulate mood, stress, and cognitive function.
- Adequate sleep supports the brain's ability to repair and regenerate cells, contributing to overall brain health.
Brain Functions Influenced by Sleep
- Sleep helps regulate the circadian rhythm, which controls the sleep-wake cycle and influences energy levels throughout the day.
- Memory consolidation occurs during sleep, where the brain processes and stores information acquired during wakefulness.
- Sleep is essential for emotional regulation, with insufficient sleep leading to increased irritability and mood swings.
- Brain plasticity, the brain's ability to adapt and change in response to experiences, is enhanced during sleep, promoting learning and cognitive flexibility.
Sleep Deprivation and Cognitive Function
When it comes to cognitive function, sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain performance. Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on cognitive abilities, affecting various aspects of mental processes.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Abilities
Sleep deprivation can lead to impaired cognitive function, making it difficult for individuals to focus, learn, and make decisions. Lack of sleep can affect memory consolidation, attention span, problem-solving skills, and overall cognitive performance.
- Memory Consolidation: Sleep is essential for the brain to consolidate and store memories. Sleep deprivation can interfere with this process, leading to difficulties in retaining and recalling information.
- Attention Span: Adequate sleep is necessary for sustaining attention and concentration. Sleep-deprived individuals may experience difficulties in staying focused on tasks and processing information efficiently.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Lack of sleep can impair problem-solving abilities and critical thinking skills. Sleep-deprived individuals may struggle to find creative solutions to challenges and make sound decisions.
Memory Consolidation During Sleep
Sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, which is the process of stabilizing and organizing memories to enhance long-term retention
Relationship Between Sleep Stages and Memory Formation
Different stages of sleep, such as slow-wave sleep (SWS) and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, are associated with specific aspects of memory consolidation. SWS, characterized by deep and restorative sleep, is linked to the consolidation of declarative memories, which are facts and events.
On the other hand, REM sleep is believed to be crucial for the consolidation of procedural memories, such as motor skills and emotional memories.
- SWS and Declarative Memory: During SWS, the brain replays and strengthens newly acquired memories, transferring them from short-term storage to long-term storage. This process is essential for the retention of factual information.
- REM Sleep and Procedural Memory: REM sleep is associated with the integration of procedural memories, allowing individuals to improve motor skills and consolidate emotional experiences. This stage of sleep is vital for learning complex tasks and emotional regulation.
Studies Linking Sleep to Memory Retention
Research has demonstrated the significant impact of sleep on memory retention through various studies. For example, a study published in the journal Nature Neuroscience found that participants who experienced SWS after learning a new task showed better retention compared to those who did not experience this stage of sleep.
Additionally, studies using brain imaging techniques have revealed increased activity in brain regions involved in memory consolidation during sleep, further supporting the relationship between sleep and memory formation.
Brain Detoxification During Sleep
During sleep, the brain undergoes a crucial process known as brain detoxification. This process involves clearing out toxins and waste products that have accumulated in the brain throughout the day.
The Importance of Sleep in Clearing Out Toxins
- Sleep allows the glymphatic system to work efficiently, which is responsible for flushing out waste from the brain.
- During deep sleep stages, the space between brain cells increases, allowing for the removal of toxins such as beta-amyloid, a protein associated with Alzheimer's disease.
- Proper brain detoxification during sleep is essential for maintaining cognitive function and overall brain health.
Impact of Lack of Sleep on Brain Detoxification
- Chronic sleep deprivation can impair the glymphatic system's function, leading to a buildup of toxins in the brain.
- Studies have shown that inadequate sleep is linked to an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases due to the lack of efficient brain detoxification.
- Individuals who consistently experience poor sleep quality may struggle with cognitive decline and memory problems as a result of impaired brain detoxification processes.
Summary
In conclusion, the profound impact of sleep on long-term brain health cannot be overstated. By understanding the significance of a good night's sleep, we pave the way for enhanced cognitive abilities and overall brain health.
FAQ Insights
How does sleep affect long-term brain health?
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining cognitive function and overall brain health. It allows the brain to consolidate memories, clear out toxins, and rejuvenate for optimal performance.
What are some cognitive functions influenced by sleep?
Sleep influences cognitive functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, creativity, and emotional regulation.
Can lack of sleep impact memory retention?
Yes, insufficient sleep can impair memory retention as the brain is unable to effectively consolidate and store memories during the different stages of sleep.